Github For Dummies
This is the transcript of my seminar on Github for Dummies.
Git was created in 1995 by Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux, when he was frustrated by existing version control systems. But what exactly is a version control system?
Suppose you are working on a huge software project, and at some point, after making several changes you run the program and it just crashes. You had closed all your editors before so you can’t hit Control-Z and simply undo your changes. What do you do now?
The correct answer is: run it again and again until it works. To avoid a situation like this, you should use git. With git you can commit your changes which means you can create a checkpoint , which can be reset to later, if the need arises. Lets see how this is done.
Open up your git-bash or any shell that has git installed. Now cd into the directory where you want to initialize your git repository and hit git init. If you see something like Initialized empty Git repository in path, this was successful. Now this git repository will track any changes you tell it to within this directory.

Now lets write a script that shows us the current time.
from datetime import datetime
now = datetime.now()
print(now.strftime('%H:%m'))
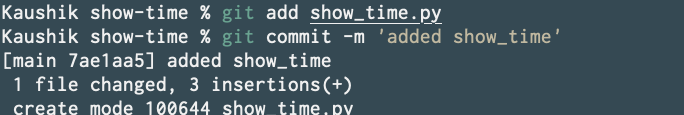
Great now lets make a commit by first adding it to the stage using git add and then commit your stage using git commit.
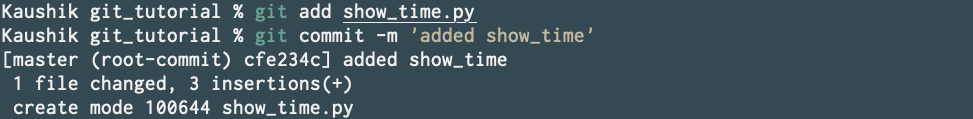
Great. You’ve made your first commit.

AHHHHHHHHH I deliberately deleted my script using rm. The shell has nothing like Recycle Bin, OH NO What do I do now?!
Your commits are identified by their hashes. To grab this previous commit’s hash hit git log.
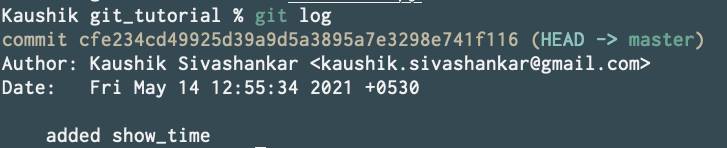
So my commit’s hash is cfe234cd49925d39a9d5a3895a7e3298e741f116. Yours will differ.
Now you can reset to this commit using
git reset --hard cfe234cd49925d39a9d5a3895a7e3298e741f116
Awesome we have our show_time back.

Now what if you made a commit you didn’t mean to make? How would you delete this commit without hard resetting to it? Simple. You soft reset.
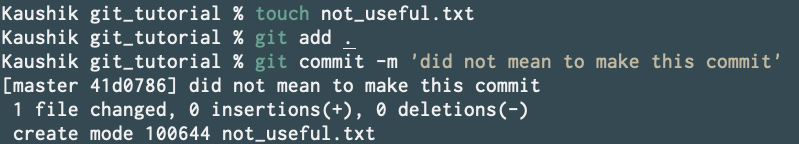
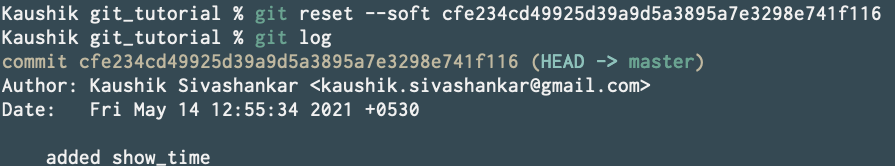
So now run git log to grab the hash of the commit you want to soft reset to.
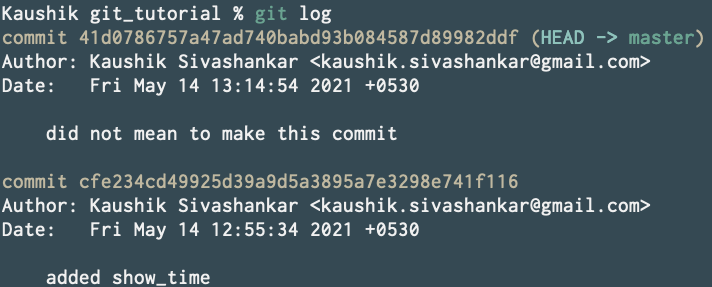
So once more we want to soft reset to added show_time commit. So simply run
git reset --soft cfe234cd49925d39a9d5a3895a7e3298e741f116
Running git log again can verify that we have deleted that commit.
Now lets move to Github!
First off, if you don’t have dark mode on, quickly click the button on google meet that looks like a red sideways telephone.
Otherwise we can proceed to cloning someone’s repo! First copy the repo url.
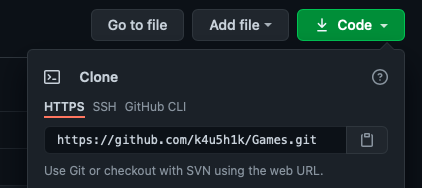
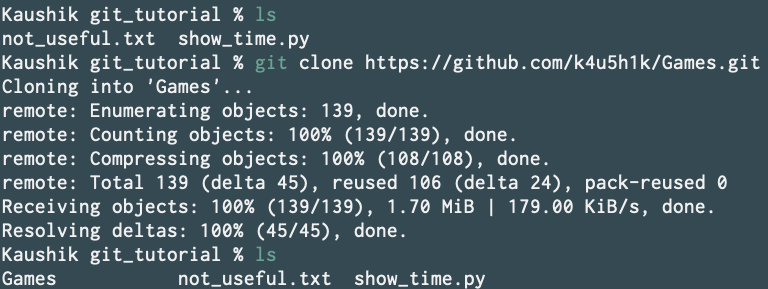
then hit git clone https://github.com/k4u5h1k/Games.git to clone the repo within the current directory.
Now lets each make a github repo of our own and clone them. To make a repo hit the plus on the top right and click on new repository.
Fill in the details and hit Create repository.
You have created your first repository.
Looks good. Lets clone this.
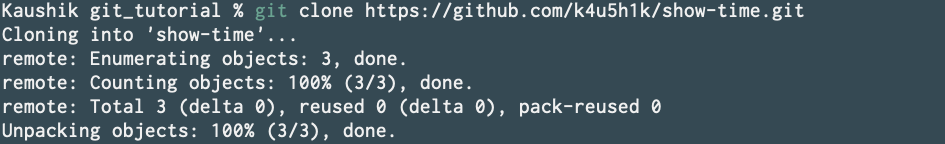
Now move your show_time script into our cloned directory.
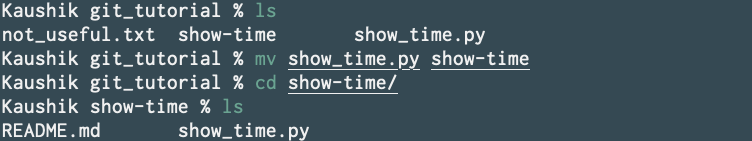
Now make a commit.
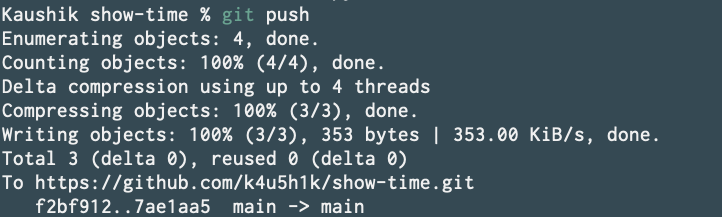
And push it to github using git push.
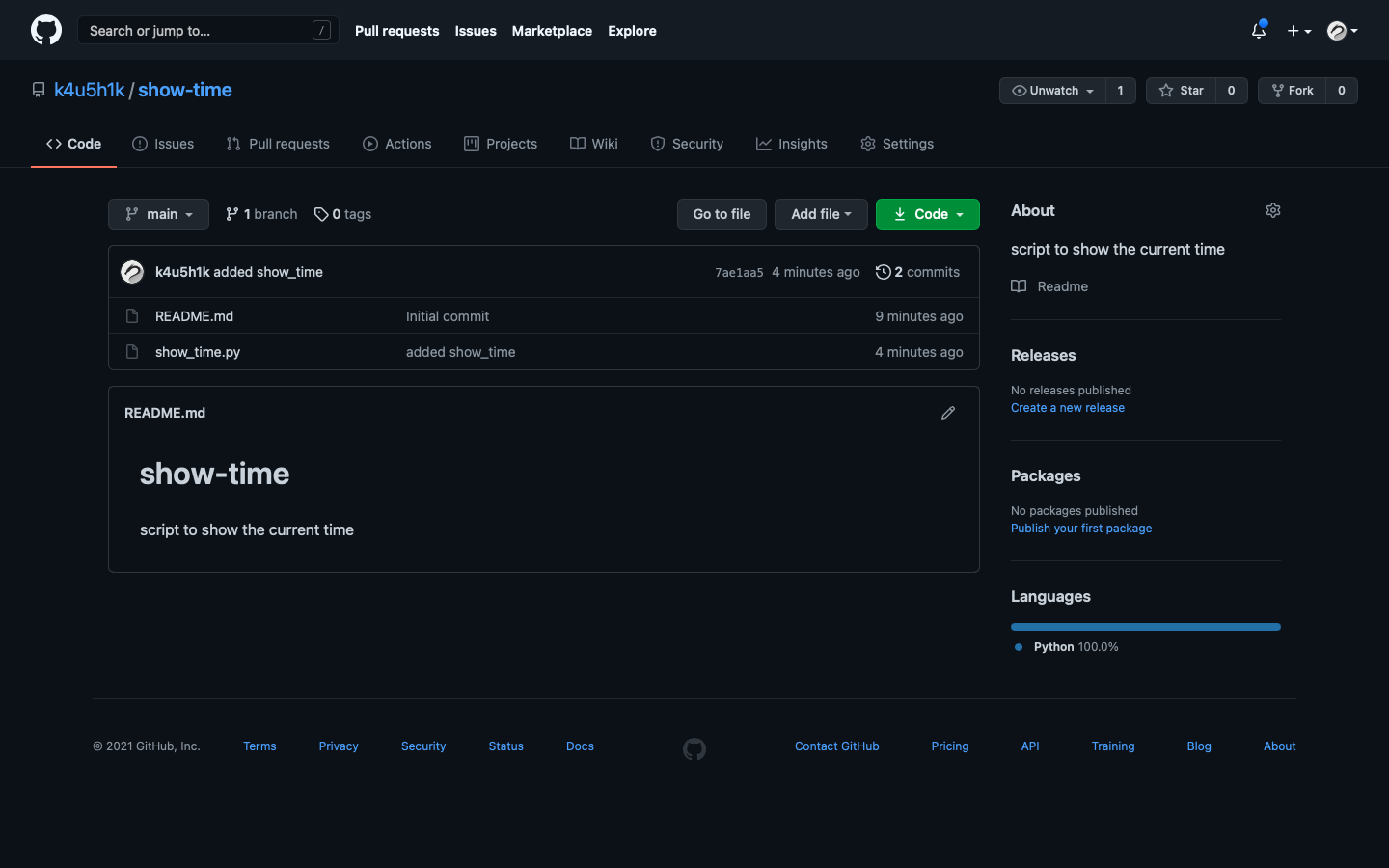
Now you can refresh your github repo page and show_time.py should appear.
Now what if we want to work with someone else’s repository. To do this we have two options.
-
Simply clone their repo locally and use their code however you want.
But in this option you will not be able to push to github because you are not allowed to push to their repo.
-
Create a fork
forking a repo means creating a copy of the original repo in your account. This will allow you to make changes to the code and push it to your fork without affecting the original repository.
To fork a repo you can click on the fork button on the top right
Now create a fork of the DNT apis repo. Go to https://github.com/dreadnoughtrobotics/DNT-apis and hit fork.
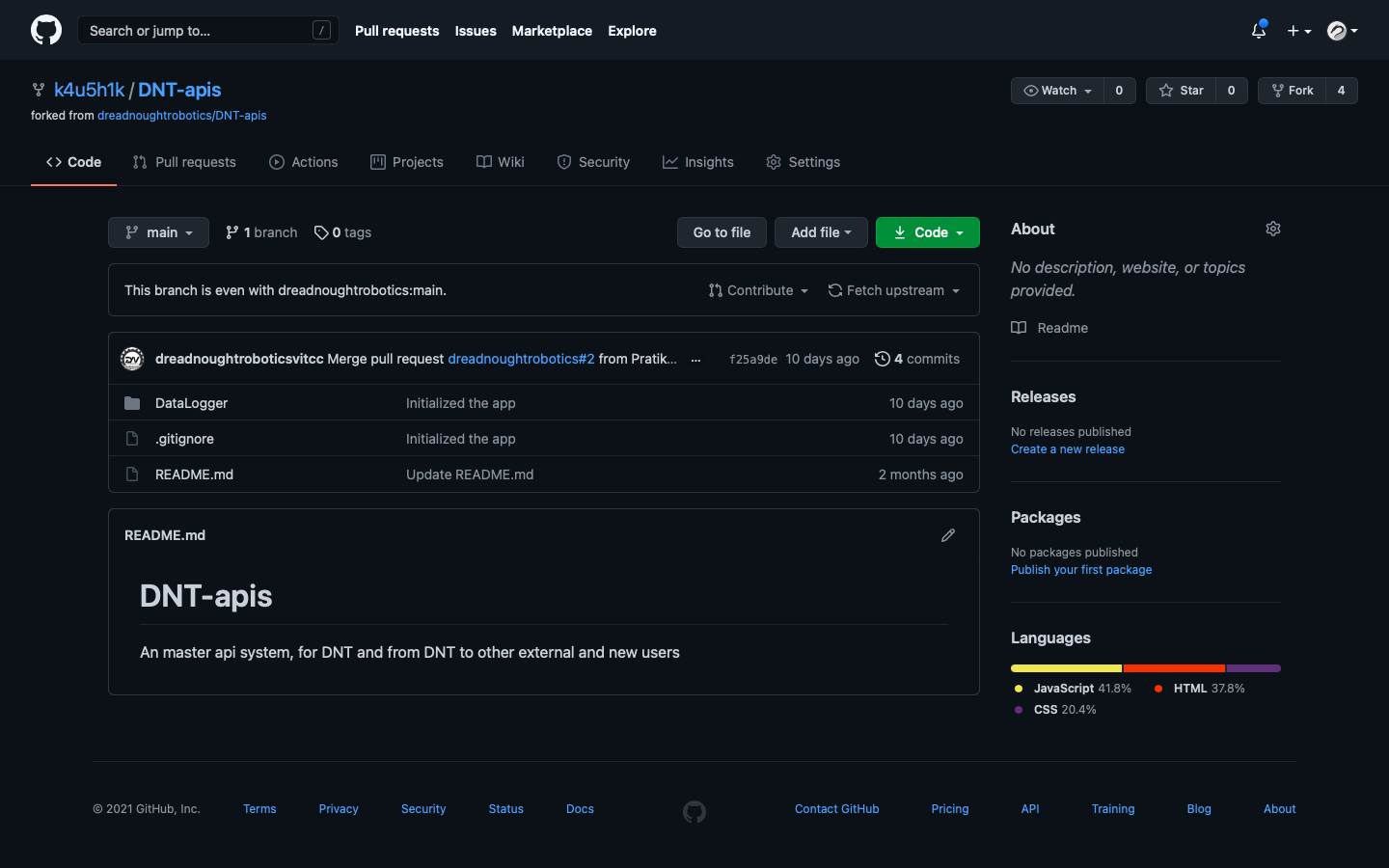
This should create a fork of the original repo in your account. You can now clone this repo and make whatever changes you want.
But what if you have made a change or wrote a new feature that you think will benefit our origin repo? You make a Pull Request (PR).
Once you make your PR the maintainers will review it, or suggest changes if required. Finally they may merge your PR or close it without merging, if they found your addition inappropriate or inadequate.
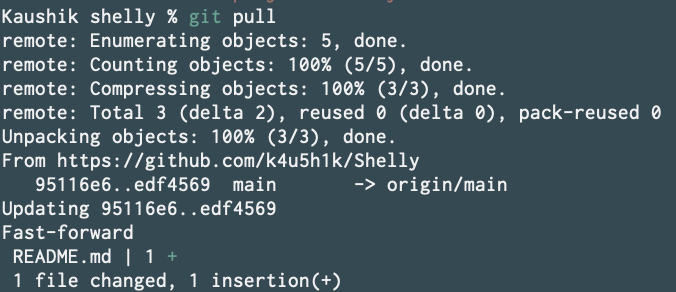
Now if someone makes a PR to your project and you accept their changes, how will you apply their changes to your local code? Will you clone the repo again? No. You use git pull.
Lets make a change to our screen_time repo’s README and pull the change locally.

Click on the pen icon here and make changes to the README.
Then go to your screen_time directory and type git pull to get those changes in your local README.
You are now equipped with the power of git!